Provider of Advanced CT Scan Software & License Activation Solutions
Seeking dependable resources to support your CT imaging systems? We provide:
Efficient license activation for CT scan software across leading platforms. License Option Generation for critical modules, including: Advanced Reconstruction, Cardiac CT, Neuro Perfusion, Dose Optimization, and Metal Artifact Reduction—covering console, workstation, and enterprise viewer deployments.
Our offerings are tailored to clinical teams, ensuring seamless uptime, full compliance (DICOM/IHE), and optimized diagnostic performance.
📩 For additional details, connect with us via WhatsApp: +967 775455559
Direct link: https://wa.me/message/NRDFVKNYDTUNM1
Allow us to help you maximize the capabilities of your CT imaging equipment! 🌟

Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Every minute of scanner downtime risks delayed diagnoses and lost revenue. If you need to buy CT scan license and software, this guide shows exactly what to choose, how to activate it, and what it should cost. We’ll compare perpetual vs. subscription licenses, explain add-on modules and trials, and walk through online/offline activation and verification. You’ll see pricing/TCO drivers, common troubleshooting fixes, and the compliance essentials (DICOM/IHE, FDA/CE, HIPAA/GDPR). Real mini-cases and PAA answers keep it practical—so you can deploy confidently, stay audit-ready, and optimize performance today.
What Counts as a CT Scan License? (Concept & Scope)
A CT scan license is more than a serial number—it’s a set of software entitlements that determine which reconstruction tools, clinical applications, and viewing privileges your team can use. Understanding what a license actually covers, and where it technically “lives,” helps radiology managers, biomedical engineers, and IT teams budget accurately, deploy correctly, and avoid preventable downtime.
Definition & Scope of a CT Scan License
A CT software license defines feature access (e.g., iterative reconstruction, 3D MPR/VR, cardiac/perfusion, dose optimization) and usage rights (seat-based or concurrent). It may bind to a specific device, workstation, or user directory, and is delivered as a file, dongle, or cloud entitlement. Licenses also govern updates, support SLAs, and security patches that keep systems stable and audit-ready.
Consider a mid-size hospital enabling cardiac CT. The purchasing team requests entitlements for coronary analysis and advanced reconstruction, plus five concurrent viewer seats. Once installed, technologists can run high-resolution studies without bottlenecks, while radiologists access toolsets from approved stations. Because the license explicitly includes maintenance, future software fixes and minor upgrades roll in without renegotiation.
Where Licenses Run: Console, Workstation, PACS/Cloud
Scanner console & post-processing workstation. Many licenses activate on the acquisition console for immediate reconstruction, while advanced apps live on a dedicated workstation. This separation keeps scanning continuous and offloads heavy rendering to a powerful node. Example: trauma CTs reconstruct on-console for rapid triage, then complex 3D/VR runs on the workstation for surgical planning—both enabled by the same entitlement bundle.
Enterprise viewing (PACS/VNA) & cloud. Viewer licenses control how many clinicians can open exams simultaneously and which advanced tools are available in the viewer. In VNA or cloud setups, entitlements may be centrally managed, enabling secure remote reading and elastic scaling. One regional network cut report turnaround by 20% after moving to a concurrent-seat viewer license—radiologists in satellite clinics could launch DICOM studies instantly within IHE-aligned workflows.
Why Buy Genuine CT scan license ?
Choosing genuine CT scan license is not a formality—it’s the foundation for dependable imaging, predictable workloads, and audit-ready operations. Licensed software unlocks the full performance of reconstruction engines and clinical applications while preserving eligibility for updates and vendor support. Below, we explain how authenticity directly improves reliability and why it’s essential for regulatory compliance and successful inspections.
Reliability & Performance
Licensed CT software ensures algorithms—such as iterative reconstruction, metal-artifact reduction, and advanced 3D MPR/VR—run exactly as designed. This translates into consistent image quality, shorter reconstruction times, and fewer workflow interruptions. Unofficial keys often break after updates, disable features unpredictably, or block hotfixes, causing delays when you can least afford them—during peak lists or urgent trauma reads.
A community hospital that standardized on genuine licenses reported markedly smoother lists after a platform upgrade: reconstruction queues cleared faster, viewer crashes disappeared, and technologists no longer worked around disabled options. With official entitlements, the IT team could apply patches on schedule, returning the system to service without risky rollbacks or ad-hoc “fixes.”
Compliance & Audits
Healthcare regulations (e.g., FDA/CE requirements) and privacy frameworks (HIPAA/GDPR) expect verifiable, authorized software in clinical use. Genuine licenses provide traceable entitlement files, version alignment, and audit logs—evidence that inspectors and internal governance teams rely on. This documentation also preserves warranty coverage and access to vendor support when issues arise.
One regional network avoided penalties during a surprise inspection by presenting a centralized license registry: device serials, entitlement IDs, activation dates, and change history mapped to each scanner and workstation. When auditors requested proof that dose-optimization and cardiac modules were authorized, the team produced entitlement reports within minutes—turning a potential risk into a routine checkpoint.
License Types & When to Choose Each
Selecting the right CT software license affects budgets, uptime, and diagnostic capability. Licenses control which reconstruction engines, clinical apps, and viewing seats you can use—and how you pay for them. This section explains the main models, when each makes sense, and how to align choices with workload, growth plans, and governance so you avoid overspending and prevent feature bottlenecks during peak lists.
Perpetual vs. Subscription
Perpetual licenses are a one-time capital expense that grants indefinite use, typically paired with optional annual maintenance (updates/support). They suit stable, high-volume departments that rely on constant access to premium features (e.g., iterative reconstruction, perfusion). The predictability of ownership simplifies budgeting and change control, and avoids renewal risk—ideal for core scanners that must remain fully featured year after year.
Subscription licenses convert cost to operating expense with timed entitlements and built-in updates. They fit sites with variable demand, evolving service lines, or multi-site networks piloting new modalities. Subscriptions let you scale seats/modules up during seasonal spikes (e.g., trauma season) and scale down later. A regional provider, for example, subscribed to advanced cardiac CT for 12 months while evaluating long-term demand before committing capital.
Add-On Modules & Viewer Seats
Add-on licenses unlock specific capabilities—cardiac CT analysis, neuro perfusion, metal-artifact reduction, dose optimization—or advanced 3D MPR/VR toolsets. Seats can be named (assigned to users) or concurrent (pooled). Choosing the right mix prevents contention at reading time and ensures technologists and radiologists have the exact tools they need without paying for unused features across the fleet.
A practical path is to license premium reconstruction at the console and advanced analytics on a post-processing workstation, then add concurrent viewer seats in PACS for enterprise access. One orthopedic center started with base reconstruction but later added metal-artifact reduction and surgical planning modules; planning time shortened and first-read confidence improved, without replacing hardware or over-licensing every station.
Trials & Pilots (30–90 Days)
Time-boxed trials reduce risk by validating workflow fit, image quality, and reader acceptance before purchase. Define success criteria up front: reconstruction time targets, dose benchmarks, reading throughput, and clinician satisfaction. Coordinate with IT for version alignment and security, and run the pilot on representative cases (e.g., coronary CTA, stroke, oncology staging) to gather meaningful evidence.
A hospital evaluated a 60-day cardiac CT package on one scanner and a shared workstation. They tracked case mix, reformat turnaround, and report addenda rates, plus feedback from cardiology and radiology. With clear gains in throughput and fewer re-reads, procurement moved forward—this evidence-based approach justified the spend and simplified change management during rollout.

How to Buy CT Scan License and Software (Step-by-Step)
Buying the right CT scan license and software is a structured process. A clear scope, an authorized reseller, and a disciplined delivery plan protect uptime, budget, and compliance. Use the steps below to avoid over-licensing, version mismatches, and activation delays—so your scanners, workstations, and enterprise viewers go live smoothly and stay audit-ready.
1) Scope & Bill of Materials (BOM)
Start by documenting scanner model/serial, current software version, desired modules (e.g., cardiac CT, neuro perfusion, metal-artifact reduction), and the number/type of viewer seats (named vs. concurrent). Add infrastructure details—PACS/VNA, storage tiers, HA/DR, network bandwidth—and any regulatory or cybersecurity constraints. Engage clinical leads to define success metrics: image quality targets, reconstruction times, and reading throughput.
Example: a three-site network scoped two console entitlements, one high-spec post-processing workstation, and 12 concurrent PACS seats with cardiac/perfusion modules. Aligning the BOM to real case-mix data prevented overbuying by 18%, while guaranteeing enough seats for peak lists and after-hours reads.
2) Authorized Reseller Process
Work only with authorized resellers or the OEM. Request a formal quote that itemizes modules, seats, maintenance, SLAs, and delivery method (license file/dongle/cloud). Ask for compliance artifacts: DICOM/IHE conformance statements, supported versions, and security patch cadence. Insist on entitlement IDs, activation instructions, and contact paths for escalation.
A diagnostic center that purchased from an unverified seller received a blacklisted key and lost two days of service. After switching to an authorized partner, they obtained a valid entitlement within 24 hours and restored full functionality—plus access to updates and official support.
3) Contracting & Delivery
Define commercial terms (perpetual vs. subscription), maintenance & support coverage, and training. Plan a controlled rollout: version alignment, test environment, acceptance criteria (e.g., VR/MPR performance, dose-report integrity), and a rollback plan. On delivery, perform UAT (sample studies, load tests), verify license logs, and capture a change-control record for audits.
Typical timeline: Week 0–1 scoping/BOM; Week 2 quote & security review; Week 3 PO & scheduling; Week 4 install/activate/UAT; Week 5 go-live and staff enablement. Post-go-live, schedule a 30-day review to confirm KPIs and close any seating or workflow gaps.
Need help scoping, purchasing, and activating genuine CT licenses? Message us on WhatsApp: +967 775455559 for a fast, compliant quote.
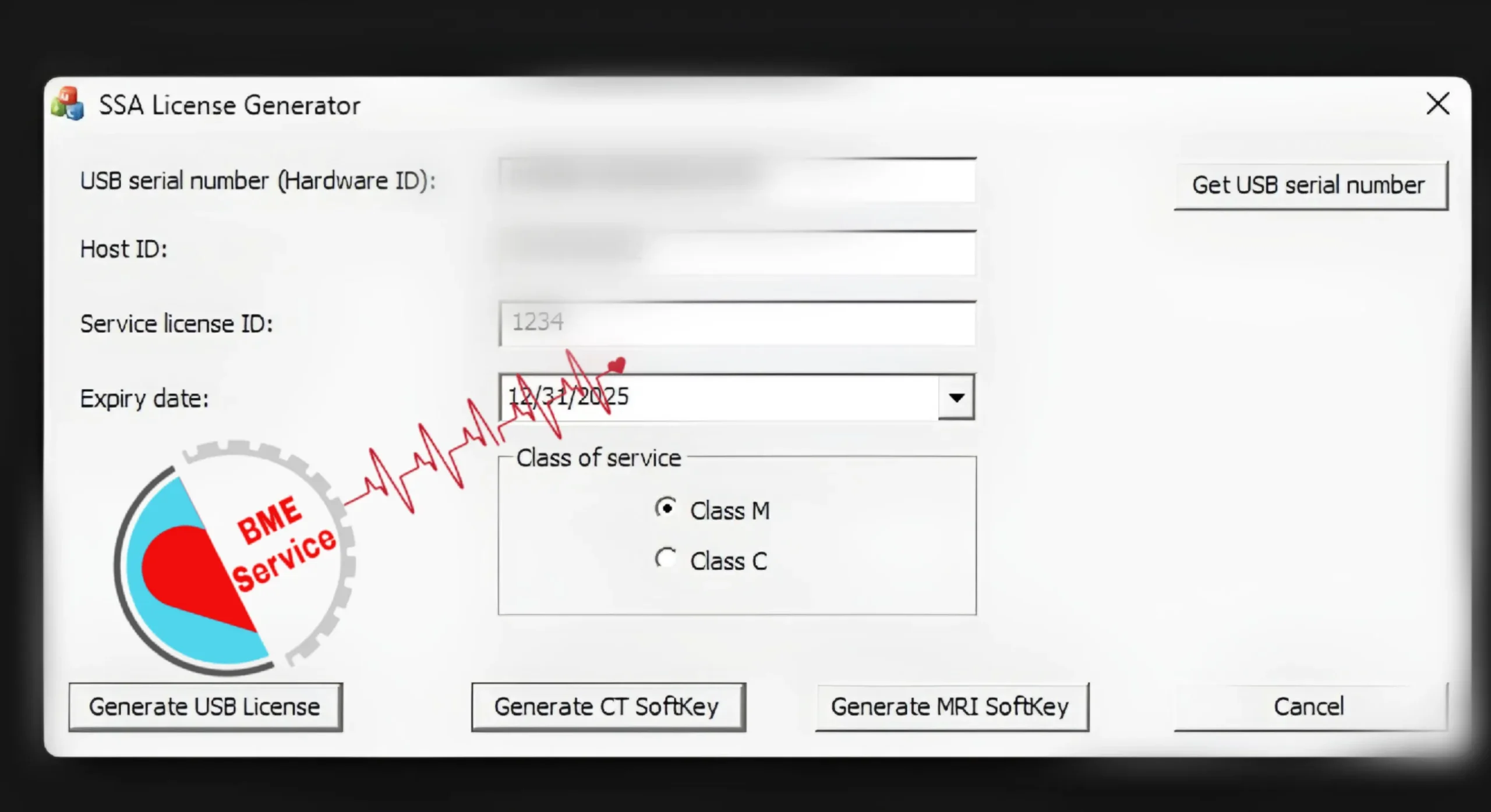
Activation & Verification (Online/Offline)
Correct activation determines which reconstruction engines, clinical apps, and viewer seats are available on day one. This section explains how to activate CT scan license and software securely in online and offline environments, then verify entitlement and version alignment. Following these steps prevents feature lockouts, avoids audit findings, and ensures your scanner, workstation, and PACS viewers are fully licensed and ready for clinical use.
Online Activation (Entitlement Sync, Version Checks, Logs)
Online activation connects your workstation or console to the vendor’s licensing server to validate entitlements in real time. Beforehand, confirm OS and application versions, time sync (NTP), firewall rules, and admin privileges. During activation, the service app retrieves entitlements, binds them to the device ID, and writes confirmation to local logs. A quick restart is often required to expose newly licensed reconstruction and analytics modules.
Example: a hub hospital brought a new cardiac CT module live in under 15 minutes by pre-whitelisting endpoints and validating TLS certificates. Post-activation logs showed the expected option codes and checksum, so the team launched a test study immediately. Because network policies were prepared, there were no failed handshakes, and no rollback was needed during the evening trauma list.
Offline Activation (File Import, HW-ID Binding, Secure Sites)
Offline activation is designed for secured or air-gapped networks. The service app generates a request file containing the hardware fingerprint and version details; a licensed administrator uploads it from a safe machine to the entitlement portal and downloads a response file (license). Importing that file completes activation locally and writes a signed receipt to logs—no persistent internet connection required.
Example: a stroke center inside a locked network used offline activation to enable perfusion and dose-reporting modules. The team verified the response file’s hash before import and archived both request/response files to a read-only share. When auditors later reviewed licensing, the immutable archive plus log entries satisfied their evidence requirements without exposing the CT subnet to external traffic.
Verification & Post-Install Validation (Functionality Proof, Audit Readiness)
After activation—online or offline—verify three things: (1) license summary matches the purchase (modules, seats, expiry), (2) software version alignment (scanner, workstation, viewer) to prevent “key not recognized,” and (3) functionality proof via test studies (e.g., cardiac CTA with iterative recon, 3D MPR/VR). Capture screenshots and export license/health reports for change-control records.
A multi-site network standardized a 10-minute validation: open license panel, export entitlement report, run a small DICOM dataset through the newly licensed workflow, and confirm timestamps in system logs. They store evidence in a central “license health” folder with renewal reminders. Result: fewer midnight lockouts, faster root-cause analysis, and smooth passage through annual compliance inspections.
Pricing & Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
License price is only part of the equation. The real cost of CT scan license and software emerges over 3–5 years, combining modules, viewer seats, deployment model, support, storage, and upgrade cadence. Understanding these variables helps you choose the right mix—avoiding overbuying, preventing renewal shocks, and ensuring the platform scales with your clinical demand and governance requirements.
Pricing Drivers: Modules, Seats, Deployment Model
Feature sets drive cost first. Advanced engines (iterative reconstruction, metal-artifact reduction), clinical apps (cardiac CT, neuro perfusion), and analytics add line items. Viewer access is the next lever: named seats suit stable teams; concurrent seats suit rotating readers. Finally, deployment matters—console, post-processing workstation, PACS/VNA, or cloud—each with different licensing footprints and performance expectations.
Example: a trauma center licensed premium reconstruction on the console for speed, placed advanced analytics on a single high-spec workstation, and chose 10 concurrent enterprise viewer seats. That architecture met peak demand without licensing every desk, trimming spend while keeping urgent lists moving and 3D planning responsive for surgeons.
Support Level, Compliance & Infrastructure Costs
Maintenance (updates, hotfixes, vendor support SLAs) is a recurring cost that protects uptime and audit readiness. Higher SLAs cost more but shorten response times and include proactive patches—valuable for sites with tight quality metrics and external inspections. Compliance work (audit logs, change control, secure deployment) adds modest process cost but reduces regulatory risk and unplanned downtime later.
Infrastructure influences the total bill. Dose archives, recon caches, and high-availability (HA/DR) storage tiers are often excluded from “software only” quotes. A regional network budgeting early for VNA capacity and encrypted backups avoided emergency storage purchases mid-rollout and sailed through a privacy review because retention, failover, and evidence logs were in place from day one.
TCO Modeling: 3–5 Year View (Perpetual vs Subscription)
Perpetual licensing front-loads spend (CapEx) and pairs with annual maintenance; it pays off in steady, high-volume services where the feature set won’t change much. Subscription shifts to OpEx, bundling updates and letting you scale seats/modules with demand—useful for pilots, seasonal load, or evolving service lines. Model both paths with realistic utilization and upgrade cadence.
A hospital compared scenarios: perpetual for core reconstruction + maintenance, and a 36-month subscription for cardiac/perfusion while demand matured. Three years later, analytics showed sustained cardiac volume; they converted the subscription to perpetual at renewal, lowering steady-state cost while preserving the ability to add new modules on subscription during future trials.
Scaling, Multi-Site Discounts & Rightsizing
Vendors often provide price breaks for multi-site bundles, enterprise viewer pools, or module packs. Consolidating requests across departments (ED, oncology, cardiology) increases negotiating power and simplifies version alignment. Centralizing entitlement management also reduces duplicate purchases and smooths license transfers during hardware refreshes (where allowed).
Rightsizing prevents silent waste. One imaging group audited usage logs and found peak concurrency at 14, not the 22 seats they were paying for. They reduced enterprise viewer seats, reinvested the savings into metal-artifact reduction, and cut re-scans on orthopedic cases—improving quality while keeping the budget flat.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
Even well-planned deployments can hit licensing snags that stall scanning or delay reads. Most problems trace to version mismatches, expired entitlements, hardware/dongle faults, or viewer seat limits. This section explains how to diagnose each issue quickly, apply a safe fix path, and prevent recurrences with simple controls—so your CT scan license and software stays stable during peak clinical hours.
Version Mismatch / “License Key Not Recognized”
A mismatch occurs when the installed CT console/workstation/viewer version doesn’t align with the license entitlement. The symptom is a rejected key or missing features after “successful” activation. Start by exporting the license summary and software build numbers, then compare them against the entitlement document; align versions (or request a reissued entitlement) before reattempting activation.
Example: after a minor PACS viewer update, advanced 3D tools vanished. Logs showed the viewer was on v9.2 while the entitlement targeted v9.0. Rolling forward the entitlement (not the software) restored features instantly. Documenting a “version matrix” per device prevented repeat incidents during routine patch cycles.
Expired or Inactive Licenses
Subscription modules can expire mid-month, silently disabling cardiac/perfusion or iterative reconstruction. Inactivity also appears if activation wasn’t finalized or the system clock drifted. Create calendar reminders 30–60 days before renewal, and enable NTP time sync on all nodes. After renewal, verify the license panel and run a short test case to confirm feature availability.
A community site lost dose-report exports on a Friday afternoon due to an overlooked renewal. They enabled auto-notifications, added a quarterly “license health check,” and baked a 10-minute post-renewal validation into change control. Outcome: zero license-related outages over the next year.
Dongle Not Detected / Driver Issues
USB dongle failures stem from worn ports, unapproved USB hubs, missing drivers, or endpoint security blocking the device class. Inspect Device Manager, try a direct motherboard port, and reinstall the vendor driver. For locked-down environments, coordinate with IT to whitelist the dongle’s hardware IDs and required services.
One trauma center experienced intermittent “dongle not found” during night shifts. The culprit was a front-panel hub with borderline power. Moving the dongle to a rear I/O port and adding a short, shielded cable stabilized detection. They also stocked a spare dongle and labeled the approved ports to guide on-call staff.
Seat Exceeded / Concurrency Limits
Viewer licenses can be named or concurrent. When concurrent seats hit capacity, new sessions fail to launch or open in restricted mode. Audit session logs to identify true peak concurrency, then rightsize seats or enforce idle-timeout policies. Educate users to close inactive sessions, especially on shared reading rooms and clinics.
A regional network paid for 24 concurrent seats but peaked at 15. After enabling automatic idle timeouts and reclaiming zombie sessions, real peaks fell to 12. They reduced the license to 14 seats and reinvested savings in metal-artifact reduction—improving image quality without increasing total cost.
Corrupted / Lost License Files (Backups & Restore)
Power loss, failing SSDs, or malware can corrupt entitlement files. Maintain encrypted, read-only backups of request/response files and periodic exports of the license summary. Store one copy offsite and test restores quarterly. During recovery, validate hashes before import and capture fresh screenshots/logs for audit evidence.
After a sudden outage, a site lost access to advanced recon. Their runbook pointed to a verified backup on a write-once share; the admin restored the entitlement in minutes and appended the incident to change control. Auditors later praised the immutable backup strategy and clear recovery trail.
Pro tip: Standardize a 10-minute validation after any change—open license panel, export entitlements, run a small DICOM test, and archive logs/screenshots. This simple habit catches issues before they hit patients.

Security, Governance & Compliance
Security and governance around CT scan license and software protect patient data, preserve uptime, and prove regulatory conformity. Strong identity controls, encryption and logging, disciplined change management, and clear regulatory evidence keep audits routine rather than disruptive. This section outlines practical controls that radiology, IT, and biomed teams can implement to safeguard licensing while maintaining fast, reliable clinical operations.
Access Control & Identity Management (SSO/LDAP, RBAC, Least-Privilege)
Centralize access with enterprise SSO/LDAP and enforce role-based access control (RBAC). Grant the minimum permissions needed: technologists use licensed tools; admins handle activation; auditors read logs only. Separate service accounts from human users, rotate credentials, and enable MFA on administration consoles. These controls reduce accidental license changes and block unauthorized option activations that could breach policy.
A regional network mapped roles to tasks: “License Admin,” “Scanner Operator,” and “Audit Read-Only.” After deploying MFA and removing shared passwords, failed admin logins dropped to near zero. During a night shift incident, the on-call admin authenticated via SSO, restored a viewer seat, and left a traceable audit entry—no guesswork, no policy violations.
Data Protection & Auditability (Encryption, Backups, Logs, Patch Cadence)
Protect entitlement files and license logs with encryption in transit (TLS) and at rest on secured volumes. Maintain immutable/WORM backups of license request/response files and periodic exports of the license summary. Standardize log retention and time sync (NTP) so timestamps align across scanner, workstation, and PACS. Align your patch cadence to vendor advisories to close vulnerabilities without breaking version compatibility.
One hospital kept an encrypted, read-only “license vault” plus quarterly restore tests. When a power spike corrupted a workstation, they restored entitlements in minutes and produced hash values and log chains for the incident record. Auditors later praised the immutable backup strategy and consistent timestamps that tied events across systems.
Governance & Change Management (Version Matrix, CAB, Rollback)
Treat licensing like any clinical change. Maintain a version matrix (scanner OS, reconstruction engine, viewer build, license entitlement version). Run upgrades in a staging environment, capture screenshots of license panels, and document acceptance criteria (e.g., cardiac CT recon < X minutes). Use a Change Advisory Board (CAB), pre-approved rollback plans, and post-change validation checklists.
A stroke center scheduled a viewer upgrade across three sites. The CAB required a dry run with five test studies, export of the new license report, and a 10-minute validation (open license panel, run MPR/VR, verify logs). A subtle mismatch surfaced in staging—not production—so they reissued the entitlement first and avoided clinical downtime.
Regulatory Alignment & Evidence (HIPAA/GDPR, FDA/CE, ISO 13485)
Map controls to frameworks: HIPAA/GDPR for security and privacy, FDA/CE for clinical software compliance, and ISO 13485 for quality management. Keep DICOM/IHE conformance statements, license inventories, activation logs, and change records readily available. Your goal is traceability—being able to show who activated what, on which device, under which approved change.
During a surprise inspection, a multi-site provider produced a single PDF bundle: device serials, entitlement IDs, activation dates, CAB approvals, and conformance statements. Inspectors sampled a cardiac/perfusion module, matched entitlement to version, and closed the review in under an hour. Clear evidence turned an audit into a routine checkpoint rather than a crisis.
People Also Ask (Answer Boxes)
Clinicians and IT teams often search the same practical questions before purchasing or activating CT scan license and software. This section provides clear, snippet-ready answers—while giving enough depth to guide decisions in the real world. Use these to brief stakeholders, shape RFPs, or resolve common roadblocks without halting clinical workflows or compromising compliance.
How much does CT software cost?
Pricing depends on feature scope (e.g., iterative reconstruction, metal-artifact reduction, cardiac/perfusion), number and type of viewer seats (named vs. concurrent), deployment (console, workstation, PACS/cloud), and support SLAs. Budget across 3–5 years, not just year one. Include storage/HA, maintenance, and upgrade cadence in TCO so you avoid surprise renewals or emergency hardware buys later.
A practical approach is to build a bill of materials (BOM), then request itemized quotes from authorized resellers. One three-site network consolidated viewer seats and bundled cardiac/perfusion modules, securing multi-site discounts and lowering spend by double digits. They also locked maintenance pricing for three years, keeping patch cycles predictable and audit-ready without last-minute capital requests.
How do I activate a CT license?
For online activation, confirm version alignment, time sync (NTP), firewall rules, and admin privileges. Run the licensing utility, retrieve entitlements, bind them to the device ID, and check logs for success codes. Restart services and verify features through a short DICOM test (e.g., 3D MPR/VR) before releasing the system to clinical use.
For offline or secured networks, generate a request file with hardware fingerprint and version data. Upload it from a safe machine to the entitlement portal, download the signed response file, and import locally. Archive both files, plus screenshots of the license panel and logs, in your change-control library. This produces defensible audit evidence without exposing the CT subnet.
Is a CT workstation license transferable?
Most licenses are tied to specific hardware IDs and are not freely transferable. Transfers—often during hardware refresh or failover events—require manufacturer approval and a documented process. Expect to provide serial numbers, entitlement IDs, and proof of decommissioning, and to receive a reissued license bound to the new target device.
Plan transfers as part of lifecycle management. One hospital scheduled a workstation swap inside a change window, pre-filed the transfer request, and staged an offline activation package. The cutover took under an hour, with logs, screenshots, and CAB approval bundled into the record. Because the old machine was formally retired, there was no license duplication risk.
Perpetual vs. subscription—what’s better for small clinics?
Perpetual licensing front-loads spend (CapEx) and works well for stable clinics that need constant access to premium reconstruction and a fixed feature set. Pairing it with maintenance gives predictable patching and vendor support. Subscription shifts cost to OpEx, bundles updates, and allows easy scaling of modules/seats as demand changes.
Many small or rural clinics begin with subscription for new service lines—say, cardiac CT—while validating case mix and reimbursement. One site ran a 12-month subscription, tracked throughput and reader acceptance, then converted to perpetual for core modules at renewal. This hybrid path limited risk early and lowered steady-state cost once volumes stabilized.
How to fix “license key not recognized”?
Start with a version check across console, workstation, and viewer; mismatches are the most common cause. Compare build numbers to the entitlement document, reissue the license for the installed version, and re-import. Next, verify device binding (correct hardware ID), time sync, and that the key was not truncated or corrupted during transfer.
If the issue followed a routine update, roll the entitlement forward rather than downgrading software. One imaging center lost advanced 3D tools after a viewer patch; logs showed entitlement for v9.0 while software ran v9.2. A reissued key restored features immediately. They added a “version matrix” and a 10-minute post-change validation to prevent repeats.
Case Studies & Mini Anecdotes
Real-world outcomes help translate licensing theory into operational results. The following brief case studies show how disciplined approaches to CT scan license and software—from entitlement alignment to evidence capture—can prevent downtime, accelerate reporting, and simplify audits. Use these patterns as playbooks to guide procurement, rollout, and ongoing governance in environments where minutes and image quality truly matter.
Downtime Avoided: Version Mismatch Resolved
A metropolitan hospital lost advanced 3D tools after a routine viewer patch. Activation looked “successful,” yet the license panel flagged a silent incompatibility. The team compared build numbers to the entitlement document, discovered the key targeted an older version, and requested a reissued entitlement from the authorized reseller—restoring full functionality in under 40 minutes.
They then formalized a “version matrix” (console, workstation, viewer, entitlement) and a 10-minute post-change validation: open license summary, export logs, and process a small DICOM test. Over the next year, the site reported zero license-related cancellations, and evening trauma lists ran without emergency rollbacks or vendor escalations.
Performance Gain: Advanced Reconstruction Activated
A regional imaging network licensed iterative reconstruction and metal-artifact reduction on the console, plus advanced 3D MPR/VR on a dedicated workstation. With genuine, version-matched entitlements, median reconstruction time for standard chest CT fell from 92 seconds to 62 seconds (-33%), and first-read report turnaround improved by 18% during peak hours.
Clinicians noted clearer visualization around orthopedic hardware and fewer repeat scans. IT analytics showed viewer session concurrency smoothing after enabling enterprise seats—radiologists could open reformats immediately instead of queueing. The center codified these gains in a KPI dashboard, tying licensing costs to measurable throughput and quality improvements.
Audit Pass: Evidence, Traceability, and Speed
During an unannounced inspection, auditors requested proof that cardiac/perfusion modules were authorized and current. The site produced a single PDF bundle: device serials, entitlement IDs, activation dates, CAB approvals, and immutable (WORM) backups of request/response files with hashes. Inspectors sampled a recent activation, matched timestamps across NTP-synced logs, and closed the review in under 60 minutes.
Post-audit, the facility adopted quarterly “license health checks,” storing screenshots and exported summaries in a central repository. When a workstation was later refreshed, the documented transfer procedure (decommission proof, reissue request, offline activation) completed within one maintenance window—no duplication risk, no service interruption.
Conclusion & Next Steps (CTA)
Choosing the right CT scan license and software is a clinical and operational decision. You’ve seen what a license covers, why authenticity matters, which models fit different workloads, and how to buy, activate, verify, and govern them. Bringing these elements together—plus clear pricing/TCO and fast troubleshooting—ensures reliable imaging, smoother lists, and audit-ready evidence without last-minute fire drills.
Key Takeaways for Decision-Makers
Genuine, version-matched entitlements unlock the algorithms that matter—iterative reconstruction, 3D MPR/VR, cardiac and perfusion—while preserving patch eligibility and vendor support. Map licenses to where work happens: console for speed, workstation for heavy 3D, enterprise viewer seats for collaboration. After every change, validate with a short DICOM test and archive logs/screenshots to keep audits routine.
Plan costs over three to five years, not one. Model perpetual vs. subscription, rightsize viewer concurrency, and budget for storage, HA/DR, and maintenance SLAs. Governance closes the loop: SSO/RBAC, encrypted backups, a version matrix, and a simple “license health check” schedule. In our case studies, these habits cut reconstruction time, avoided cancellations, and shortened inspections to under an hour.
Action Plan & CTA
Start with a scoped bill of materials: scanner model/serial, software versions, modules, and seat types. Request an itemized quote from an authorized reseller, agree on support SLAs, and schedule a controlled rollout. Pre-check firewall/NTP, activate online or offline, then run a 10-minute post-install validation. Finally, centralize evidence—entitlements, logs, and screenshots—for audit traceability.
Ready to deploy with confidence? We supply original CT licenses, guide scoping, and handle activation/verification to keep your lists moving. Get a fast, compliant quote or immediate support via WhatsApp: +967 775455559. One disciplined licensing process today prevents costly downtime tomorrow—and keeps your CT service delivering at its peak.
Also read about information on CT Software License Purchase – Top Systems: Siemens &More , click here. (https://bmeser.com/ct-software-license-purchase/)





Istanbul food guide
August 17, 2025Istanbul food guide Amazing value for the price.
ebrahim
August 22, 2025There is no relation to this post, my friend. We are here providing maintenance services for medical devices
Istanbul local experience tour
August 18, 2025Istanbul local experience tour Guides are friendly and knowledgeable.
ebrahim
August 22, 2025There is no relation to this post, my friend. We are here providing maintenance services for medical devices
Buy Medical Device License – For Ultrasound, CT & MRI
August 22, 2025[…] read about information on Buy CT Scan License And Software | Secure Activation , click here. […]